Mapping Metadata
The most important feature of Capturebot is assigning metadata from your datasource to EXIF tags. This is done by mapping a source field to the destination tag.
As long the document isn't locked mappings can be added, removed, and modified.
Adding & Removing Mappings
To add a new mapping, click the + button on the right-hand side of an existing mapping, this will insert a new row below the one you selected.
To remove a mapping, click the - button on the right-hand side of a mapping. There must always be at least one mapping, so you can't remove them all.
Reordering
Mappings can be dragged and dropped to reorder them. This doesn't affect how mappings are applied, and is only a visual ordering.
Mappings
Source Field
The source field is what your original datasource calls a piece of metadata. This might be entered by hand into a spreadhseet, exported from a FileMaker database, or anything else. Each source field and be used in as many mappings as you'd like.
Conversion Mode
This is an important feature for ensuring metadata is valid. There are two options: to use the unmodified source value or to convert the value to an array.
The first does what it says on the tin: it passes the value from your datasource directly to the EXIF tag. Some values are automatically converted, like numbers for star ratings or color tags.
Converting to an Array
Convert the value to an array is used for metadata fields than can contain a list of items, like keywords or IPTC supplemental categories. Formatting metadata correctly is important for searching and ease of use later. When this option is selected a new option is added: the array delimiter.
By default Capturebot uses a comma to split strings, but the delimiter can be anything you'd like.
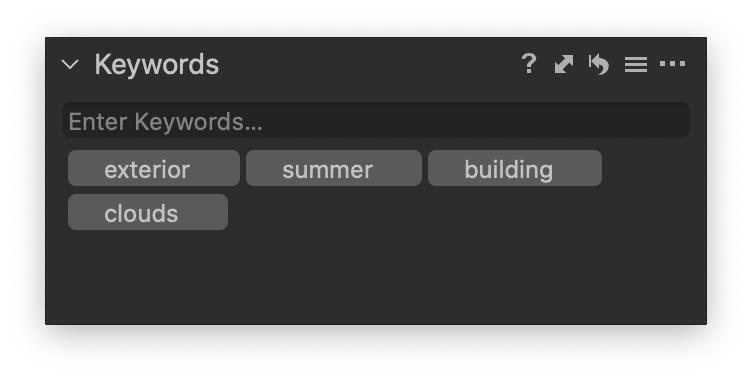
For instance, a string representing keywords exterior,summer,building,clouds would be converted into an array:
- exterior
- summer
- building
- clouds
and appear in Capture One as
Convert to a string
This simply attempts to convert the input value to a string.
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
| 5 | "5" |
| Some String | "Some String" |
Modifying String Case
Modify the case of a string by capitalizing, lowercasing, or uppercasing it.
| Modification | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Capitalize | some string | Some String |
| Lowercase | Some String | some string |
| Uppercase | Some String | SOME STRING |
Replace Occurrences
Replace occurrences of a target string with a new string. This can be used to help clean up input data.
| Target | Replacement | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| invalid | valid | some invalid string | some valid string |
Convert to a Date
Attempt to convert the source value into a date with the specified format. When assigning metadata to a date use this conversion to ensure the date is valid. The mapping will attempt to detect the kind of input data and apply valid date conversions.
If the input is a number it will be treated as a Unix timestamp.
| Format | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| yyyy-MM-dd | 2021-05-31 | Date(2021-05-31) |
| yyyy-MM-dd | 1622480643 | Date(2021-05-31) |